Hair shedding is a completely natural and expected part of the hair growth cycle. While it may seem alarming at times, it's important to understand that shedding is a sign of a healthy, functioning scalp and hair growth process. Here's a closer look at why hair shedding happens and the science behind it.
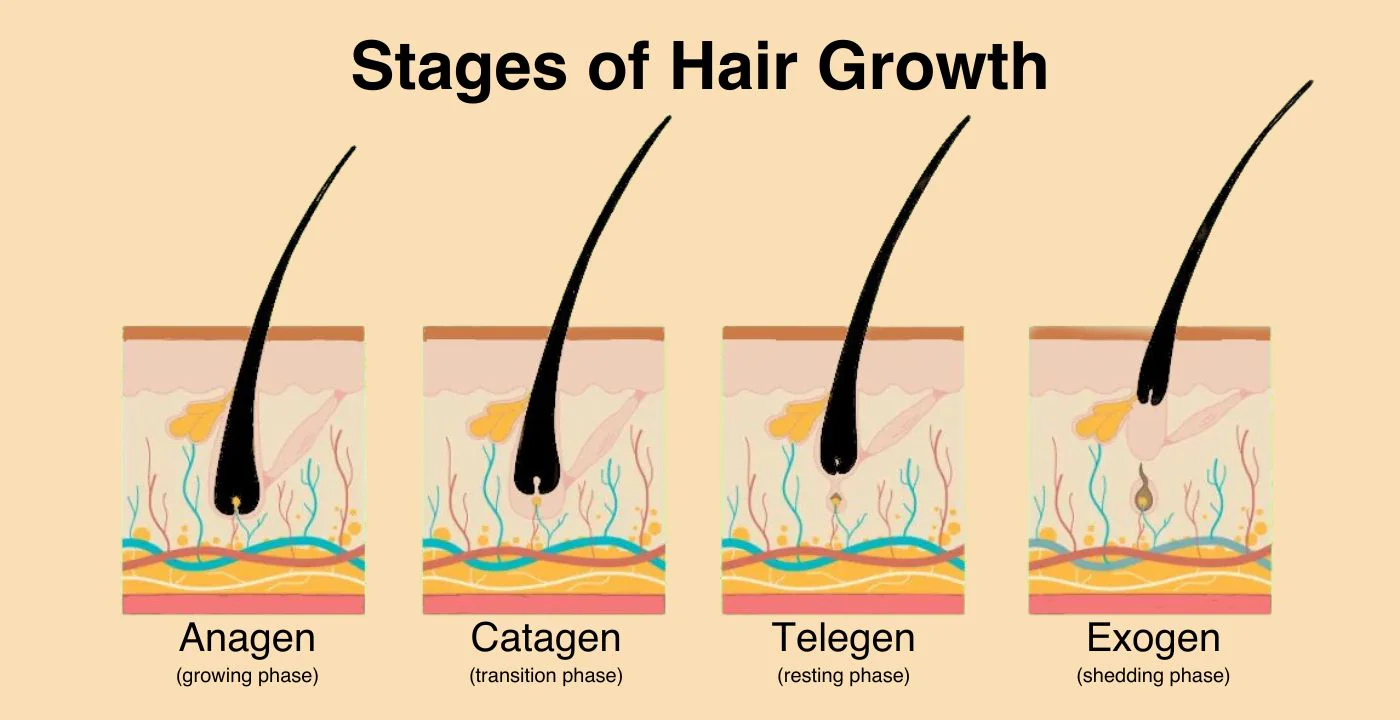
 Your hair goes through a continuous cycle of growth, rest, and shedding, which occurs in three main phases: the Anagen phase, the Catagen phase, and the Telogen phase. These phases all contribute to natural hair shedding, and understanding each of them will give you clarity on why losing some hair is completely normal.
Your hair goes through a continuous cycle of growth, rest, and shedding, which occurs in three main phases: the Anagen phase, the Catagen phase, and the Telogen phase. These phases all contribute to natural hair shedding, and understanding each of them will give you clarity on why losing some hair is completely normal.
1. Anagen Phase (Growth Phase): How Hair Grows and Is Actively Nourished
The Anagen phase is the active growth phase of the hair cycle. During this phase, hair is growing at its fastest rate, and each follicle is nourished by the scalp's blood supply. Most of your hair (around 85-90%) is in the Anagen phase at any given time.
- This phase can last from 2 to 7 years depending on genetics, and during this time, your hair is actively producing new cells, pushing older cells out, and growing longer and stronger.
- The rate of hair growth varies, but it generally grows about half an inch per month.
Since hair is actively growing during this phase, shedding doesn’t typically occur in large amounts here—unless there are external factors like stress or medical conditions disrupting this phase
2. Catagen Phase (Transition Phase): Preparing to Shed
The Catagen phase is a short transitional phase that lasts around 2-3 weeks. During this time, hair growth slows significantly, and the hair follicle starts to shrink. It’s during this phase that the hair stops actively growing, and the body begins preparing for the shedding process.
- Hair follicles begin to detach from the nourishing blood supply, and hair production slows.
- Hair will stop growing but will not yet fall out—rather, it moves into the next phase, where shedding will eventually occur.
Though shedding doesn't typically happen during the Catagen phase itself, hair is preparing to enter the Telogen phase, where it will eventually be replaced.
3. Telogen Phase (Resting Phase): Resting and Shedding Hair
The Telogen phase is the resting phase of the hair cycle, where hair is no longer growing, but it is still securely attached to the follicle. This phase lasts for about 3 months, and roughly 10-15% of your hair will be in this phase at any given time.
- During the Telogen phase, the hair follicle is at rest and not producing new hair cells.
- Eventually, the hair will detach from the follicle and shed naturally, making room for new hair to grow in the Anagen phase.
- Shedding between 50 to 100 hairs per day is normal for most people, though this can vary based on individual factors, like hair density or the time of year.
The hair that sheds during this phase is usually replaced by new growth once the hair follicle re-enters the Anagen phase.
Why Hair Shedding Is Normal
Hair shedding is simply a sign that your hair is completing its natural cycle. Your hair is constantly renewing itself, and as old strands shed, new ones grow to replace them. The average person can lose anywhere from 50 to 100 hairs per day, and it’s completely normal to experience shedding in varying amounts throughout the month.
Causes of Increased Hair Shedding:
While shedding is normal, there are times when it can increase due to factors such as:
- Hormonal changes: Pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid issues can lead to temporary shedding.
- Stress: Physical or emotional stress can trigger a condition known as telogen effluvium, where hair sheds in large amounts.
- Nutritional deficiencies: Lack of certain vitamins or minerals, like iron or biotin, can affect hair growth and lead to more shedding.
- Hair care practices: Over-styling, excessive heat, or harsh chemicals can damage hair and increase shedding.
- Medical conditions: Conditions like alopecia or scalp infections can lead to abnormal hair loss.
When to Worry About Shedding:
-
It’s important to distinguish between normal shedding and excessive hair loss. If the shedding leads to noticeable thinning or bald patches, it’s best to consult with a trichologist or dermatologist.
Conclusion: The Natural Shedding Process
In summary, hair shedding is a natural part of the hair growth cycle, and it's a sign that your hair is functioning as it should. Understanding the three phases—Anagen, Catagen, and Telogen—will help you recognize that shedding is a normal process that happens when hair follicles rest and renew. As long as shedding stays within the typical range, there’s no need to worry. However, if shedding increases suddenly or excessively, it may be worth consulting a specialist, like a trichologist, to rule out any underlying issues.






Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.